
Extreme weather events can have serious consequences for communities and individuals – loss of life and property, and disruption of daily activities. Understanding the science behind these events allows us to better predict and prepare for them.
In this blog post, we will explore the factors that contribute to extreme weather events and the methods used to predict and track them. Extreme weather events in the UK are rarer but not still occur.
Extreme weather events are defined as extreme changes in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, and wind patterns that may have significant impacts on the environment and human activities. These events can include severe storms such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards, as well as prolonged periods of extreme heat or cold. Droughts, which are prolonged periods of low precipitation, can also be considered extreme weather events.
Understanding the science behind severe weather allows us to accurately forecast and track these events which can help save lives and reduce impacts on local communities. Accurate forecasting also enables individuals and businesses to make Informed decisions about how to prepare and respond extreme weather events. It can also help us better understand the complex processes at work in our atmosphere and how they are affected by natural and human-made factors. This knowledge can inform efforts to mitigate impacts of extreme weather events and adapt to changing weather patterns.
Seasons also have an impact on these events, to understand why its warmer (in general) in summer and colder in winter see our other article.
Recent extreme weather events highlight that climate change is contributing to an increase in the frequency and intensity of such events. In the future, the impacts of climate change on extreme weather are expected to become even more pronounced, with more severe and prolonged heatwaves, droughts, and storms.
The BBC has a good article that goes into more detail on how extreme weather is connected to climate change.
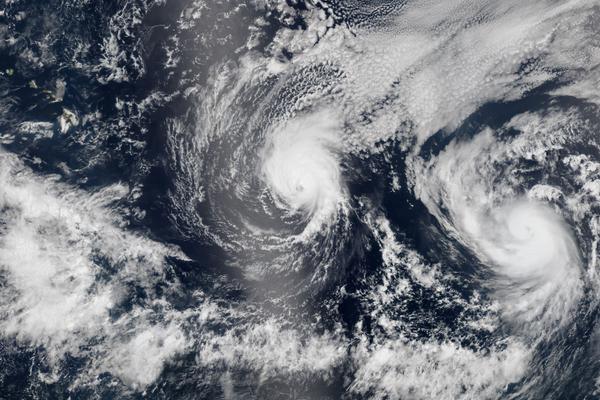
A hurricane is a tropical cyclone characterized by strong winds, heavy rain & high waves. They form over warm ocean water near the equator.
Hurricanes are categorised by their wind speed, with Category 1 storms being the weakest and Category 5 storms being the strongest. Their impact depends on wind speed and how long the hurricane remains on land.
High winds, heavy rain, flooding, and landslides result in significant damage to coastal communities and offshore infrastructure.
Weather balloon radar and satellites allow us to track hurricanes. Early warning systems and evacuation plans are critical in helping minimize the impact of these storms on local communities.
A tornado is an intense and dangerous weather event characterized by small, highly destructive storms with very high winds. These winds are caused by a rapidly rotating column of air extending from the base of the thunderstorm to the ground.
Tornadoes are most common in the central and eastern United States, although they can occur anywhere in the world. They are most likely to form in the evening or early evening and can occur any time of year, although they are most common in spring and early summer.
Tornadoes can cause significant damage to home businesses and infrastructure, uproot trees and knock down power lines, causing widespread power outages. Wind speeds can be in excess of 300 miles per hour some cases.
Tornadoes are often predicted and tracked using a combination of weather instruments and technologies such as radar weather balloons and satellites. Early warning systems and emergency preparedness plans help minimize the impact of these storms on communities.
National Geographic on YouTube has a great video on Tornadoes:
A blizzard is a severe winter storm characterized by strong winds, heavy snow and low temperatures. These storms can occur anywhere in the world, but are most common in regions with colder climates such as northern United States and Canada.
A blizzard is caused by the collision of cold and warm air masses leading to heavy snow and strong winds. These storms can last for days, wreaking havoc on transportation power and communication systems.
Blizzards can cause hypothermia & frostbite for those caught up in them and damage homes and businesses, as well as power outages.
Blizzards are often predicted and tracked using a combination of weather instruments and technologies such as weather balloon radar and satellites. Emergency preparedness plans, such as having food, water, and warm clothing on hand, can help minimize the impact of these storms on individuals and communities.
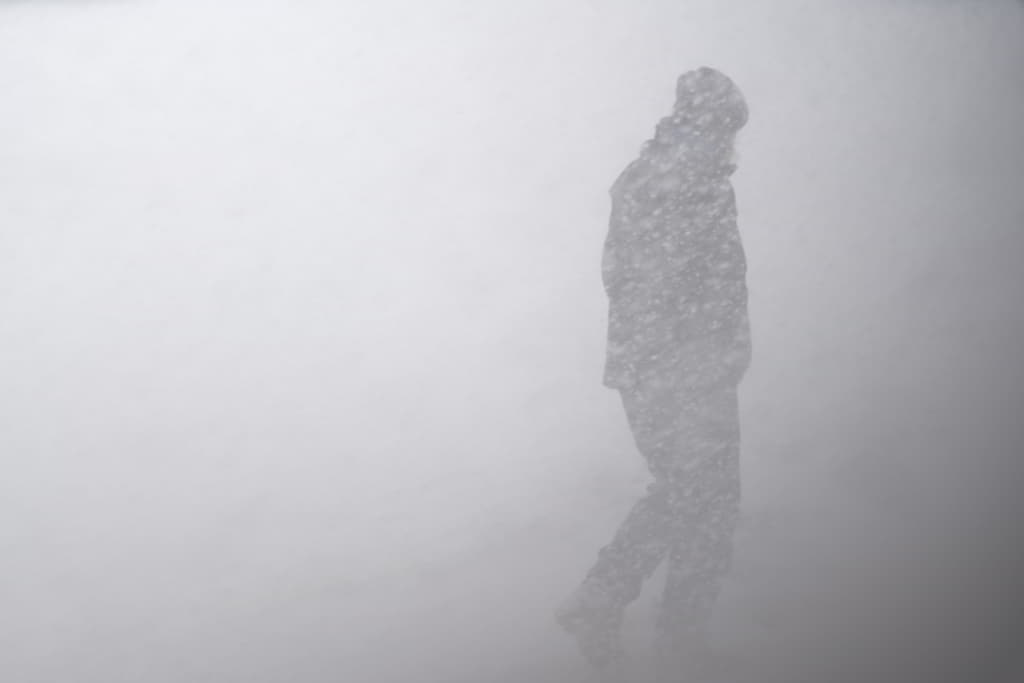

Heat waves are periods of high temperatures that can have serious consequences for human health and the environment. They are characterized by persistent temperatures that are significantly higher than average.
Heat waves can lead to a number of health problems, including heat exhaustion & heat stroke.
They also increase the risk of wildfires, can damage crops and vegetation.
Many public health authorities issue warnings and advice during heat waves so that individuals can protect themselves. Typical advice is to stay hydrated, find an air-conditioned space and avoid strenuous activity during the hottest parts of the day.
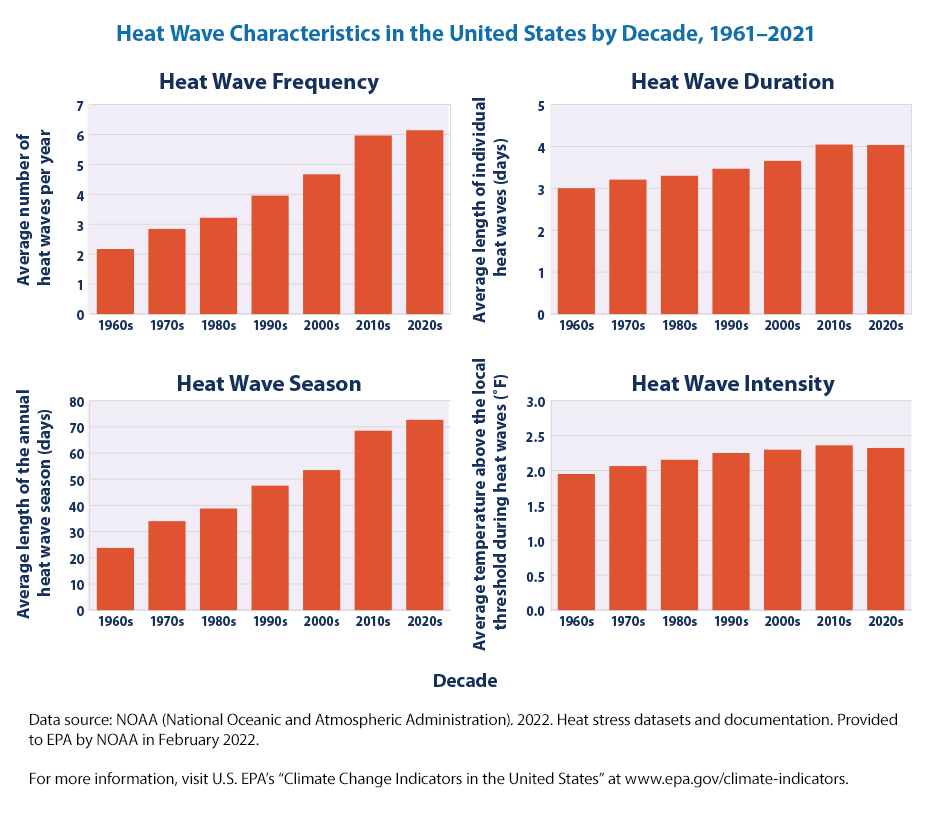
As way of an example, the following charts show the changes in frequency, duration and intensity of heatwaves in the United States, 1961-2021. Source: Environmental Protection Agency
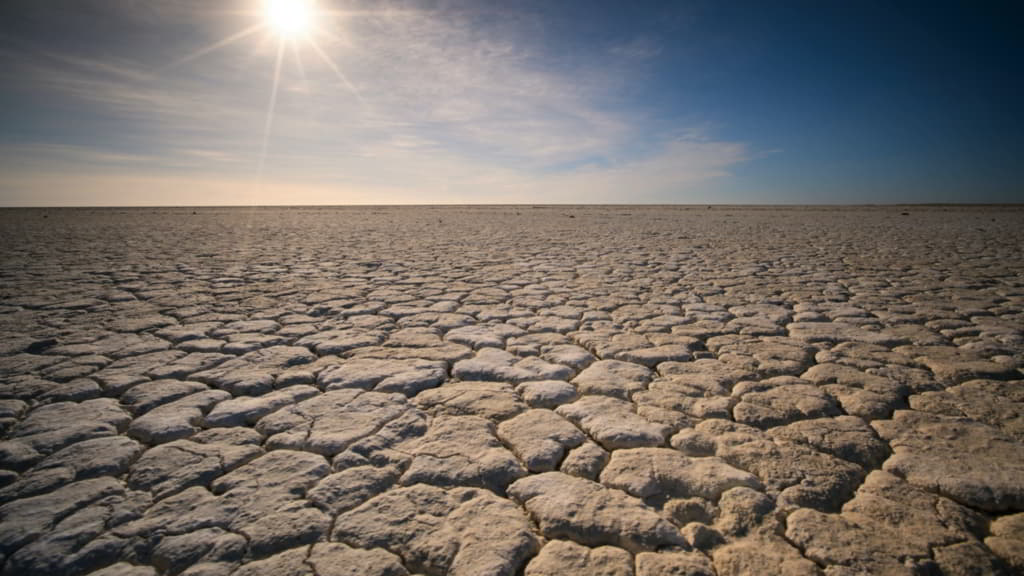
Droughts are prolonged periods of below-average precipitation which can lead to crop failure, water shortages. They can occur anywhere in the world, but are most common in areas with dry or semi-arid climates.
They can have severe consequences for agriculture and water-dependent industries such as hydropower and manufacturing.
Governments and organizations often implement drought contingency plans to mitigate the impact of these consequences . Actions such as saving water and using drought-resistant plants can also help reduce the effects of drought.

Some of the most important factors that contribute to the formation and intensity of extreme weather events include:
Temperature: Heat waves are caused by sustained high temperatures, while blizzards and cold snaps are caused by low temperatures. Air and water temperatures also affect the strength of storms such as hurricanes and tornadoes.
Humidity: High humidity (moisture content) can lead to heavy rain and thunderstorms, while low humidity can lead to drought and wildfires.
Atmospheric pressure: Low-pressure systems associated with storms bring strong winds and heavy precipitation, while high-pressure systems are usually associated with clear, dry weather.
Wind pattern: The direction and strength of the wind can affect the intensity and movement of these extreme weather events.
Topographic features: Affects the formation and intensity of extreme weather events.
There are many tools and techniques available to predict and monitor these events, including:
Meteorological instruments and techniques, such as weather balloon radars and thermometers. These tools provide detailed information on temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, and wind patterns.
Satellite and other remote sensing methods, such as radar and lidar can provide valuable data on weather patterns from a distance. They are especially useful for monitoring large-scale events such as hurricanes & snowstorms that may be difficult to observe from the ground.
Importance of accurate forecasts: Accurate forecasts are critical to ensuring public safety and minimizing the impact of extreme weather events. Early warning systems, evacuation plans and other preparedness measures can help save lives and reduce damage. Forecasting methods have improved tremendously over the years with computers and AI playing important roles.
Understanding the science behind extreme weather events is important to ensuring public safety and minimizing their impact on communities and industries. This is essential for us to adapt to and mitigate the effects of these events and to understand natural and human factors that affect weather patterns. As recent extreme weather events highlight, climate change is having a significant impact on global weather.
There is still a lot to learn about the science of extreme weather events. Ongoing research and understanding of these phenomena is critical to improving our ability to predict and respond to future impacts.